Ethereum Sharding An update planned to address the scaling issue of the Ethereum Blockchain. So, what really is Ethereum Sharding, what it aims at, what problem it will find a solution to, let’s find the answers together in this article.
In this article, we have explained for you what is Ethereum Sharding, which can be called the next big event after Ethereum’s transition from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake consensus.
What is Ethereum Sharding?
Sharding is one of the database management techniques that come to life in today’s crypto community. It is the process of splitting or horizontally splitting databases into smaller chunks or chunks. This is to allow the same thing to be carried better, to make them less heavy and easier to handle.
According to the Ethereum Foundation Blog, Ethereum Sharding is a multi-stage upgrade to improve the scalability and capacity of Ethereum. Fragmentation ensures that data storage requirements are securely distributed, making rollups even cheaper and aiming to make Nodes easier to operate.
It enables layer 2 solutions to offer low transaction fees while leveraging the security of Ethereum. This upgrade has become more of a focus since Ethereum switched to Proof-of-Stake.
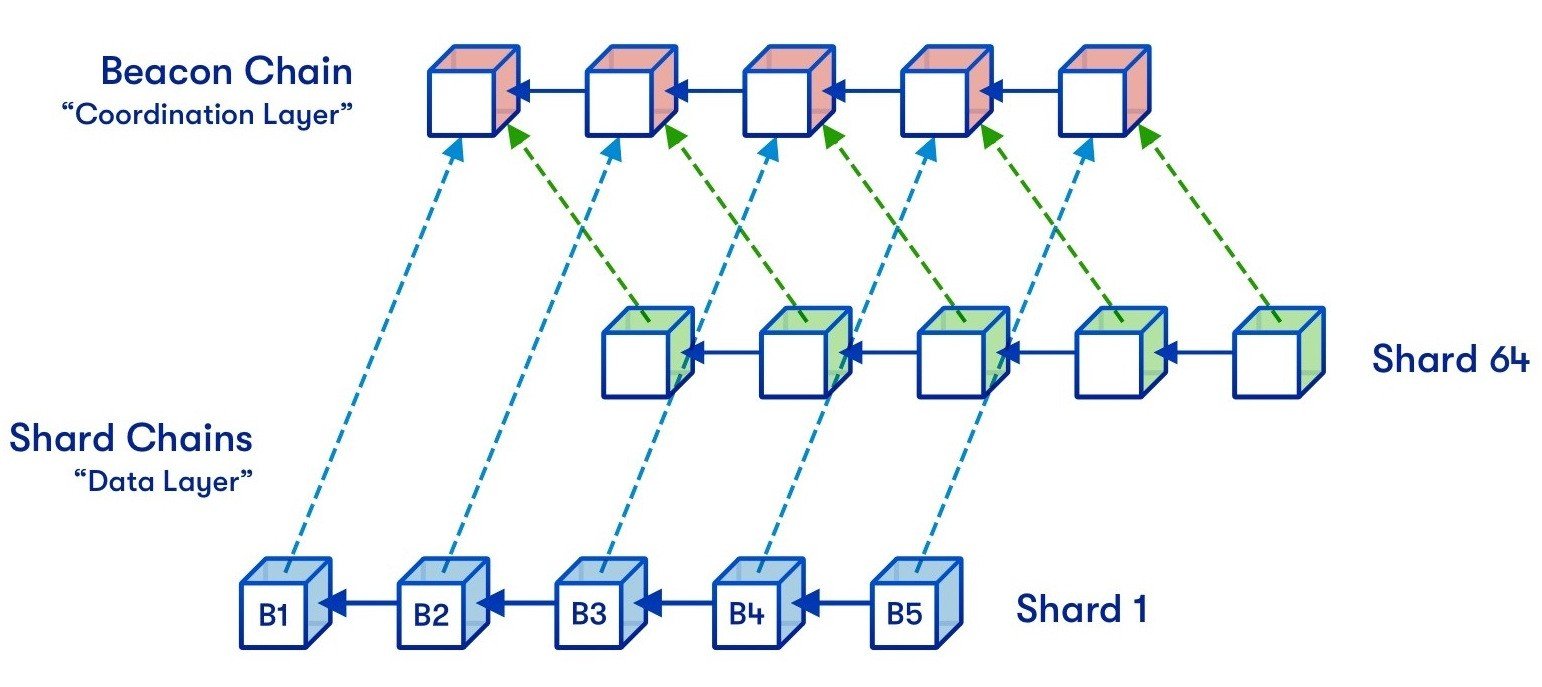
Sharding is the process of splitting a database horizontally to distribute the load. In an Ethereum context, Sharding will work synergistically with Layer 2 rollups, dividing the overhead of processing the large amounts of data needed by aggregates across the entire network. This will continue to reduce network congestion and increase transactions per second.
What Will Be the Features of Sharding?
The main advantage that sharding offers for a Blockchain is to improve scalability. Because transactions can be processed and verified faster, the time required for this process is reduced. Therefore, the network will have the capacity to process more transactions per second.
With the implementation of sharding, it will no longer be necessary to store the entire blockchain on the same node, so there will be no need to purchase expensive equipment. This ensures decentralization by enabling more people to join the network with their traditional equipment.
As an alternative to the current situation, sharding is a good way to scale if you want to keep things decentralized, as the goal is to scale up by increasing the size of the existing database. This will make Ethereum less accessible to network validators because they will need powerful and expensive computers. With sharding, validators will no longer need to store all this data themselves, but can instead use data techniques to verify that the data is made available to the network as a whole. This greatly reduces the cost of storing data at tier 1 by reducing hardware requirements.
Sharding will eventually let you run Ethereum on a personal laptop or phone. Therefore, more people should be able to join or run clients on a fragmented Ethereum. This will increase security because the more decentralized the network, the less surface area a possible attack will have.
With lower hardware requirements, sharding will make it easier to run clients on your own without relying on any intermediary service. Based on this, running more than one client will also reduce the impact of any possible error. This can aid network health by further reducing error points.




